- Photonics & Space
LabH6: Optical fibers for distributed radiation sensing
Optical fibers for distributed ionizing dose measurement
IDENTIFYING THE RADIATION-SENSITIVE OPTICAL FIBERS
While many studies have been conducted to improve (harden) the response of optical fibers to radiation, it has also been established that certain optical fibers, in particular those doped with phosphorus [S. Girard et al., JNCS, 2011] or aluminum [A. Alessi et al., PSSA, 2019] in their cores are very sensitive to ionizing (γ, X) or non-ionizing radiation (neutrons).
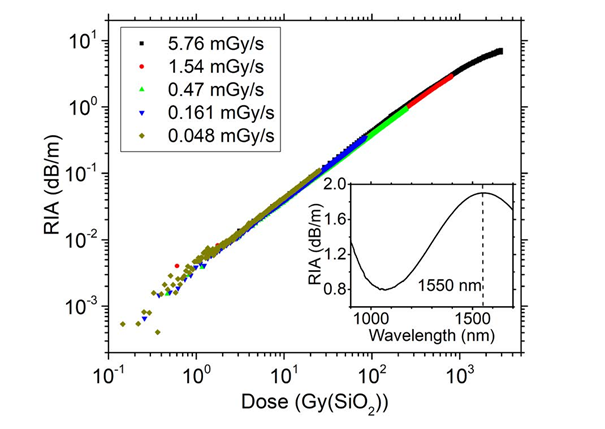
They are associated with very high levels of Radiation-Induced Attenuation (RIA) and the measurement of these optical losses, over the entire UV-IR spectral range, can thus be used to detect radiation or even to quantify the dose received (expressed in Gy (SiO2)). Studies are being conducted in close collaboration with CERN to define and qualify a distributed dosimetry solution. By combining a radio-sensitive fiber with an optical reflectometer, the dose can be measured along a fiber with a sub-metric resolution.
To design a high-performance dosimeter, these fibers should have other particular characteristics. Indeed, the RIA must not, for example, depend on the dose rate, the temperature (in the ranges targeted by the application) to ensure a reliable measurement [D. Di Francesca et al., JLT, 2019]. In view of all these parameters, the P-doped fibers are today the most promising fiber type, even if the Al-doped ones are the most sensitive [A. Alessi et al., PSSA, 2019]. The typical response of a P-doped fiber is illustrated in Fig. 1.
| COLLABORATIONS On this theme, LabH6 collaborates with CERN and Viavi SolutionsCERN is working on the design and qualification of a fiber-distributed dosimeter for implementation within its accelerators (DOFRS project: Distributed Optical Fiber Radiation Sensor). Part of the work is carried out via Gaetano Li Vecchi’s PhD thesis (UJM/CERN), in particular the calibration of the selected radiation sensitive fiber.On this subject, the partners are also working with Viavi Solutions on OTDR interrogation. A complete system for distributed and simultaneous measurement of dose and temperature has already been qualified. |
FIBER CALIBRATION FOR DOSIMETRY
Before being used as a dosimeter, the optical fibers must be calibrated in order to establish the conversion factor between the RIA and the deposited dose: this factor is expressed in dB m-1 Gy-1. A large part of these tests can be conducted at the LabHC, thanks to MOPERIX irradiation (Fig.2).
This irradiator makes it possible to submit optical fibers to wide ranges of dose (100 µGy-10 MGy), dose rates (40 µGy/s – 100 Gy/s) and temperatures (-120 °C/400 ° C). It is thus possible to establish the validity range of the sensor. The qualification of the optical fiber is generally carried out with Co60 sources or specific equipment, such as the CERN CHARM installation [D. Di Francesca et al., IEEE TNS, 2019]. After this step, the fiber optic sensor can then be deployed within the installation.
Thus, the radiation levels within the CERN Proton Synchrotron Booster (PSB) facility were measured for one year by this system, providing a spatio(1D)-temporal mapping of the deposited dose [D. Di Francesca et al., IEEE TNS, 2018].
- Optical fibers having a sensitivity of 4 dB m-1 Gy-1 at 1550 nm are available for distributed dosimetry: Radiation Sensing Fibers


